Can Your Devices Even Talk Without ARP?
Updated on June 6, 2025, by ITarian
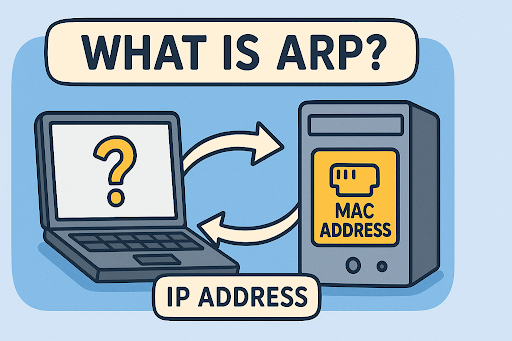
When your computer connects to a website, it happens in milliseconds—but beneath the surface, a series of protocols work together to make it seamless. One of the most critical players in that silent handshake is ARP. So, what is ARP, and why should cybersecurity professionals, IT managers, and industry leaders care?
ARP enables network devices to discover each other. But when exploited, it becomes a dangerous attack vector known as ARP poisoning. In this guide, we’ll explain the ARP protocol, explore how it works, and reveal how to secure your network against abuse.
What Is ARP?
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a network protocol used to map an IP address to a physical machine address (MAC address) on a local network. This process ensures devices can communicate on an Ethernet or Wi-Fi network, which relies on MAC addresses.
For example, if your PC knows the IP address of a printer but not its MAC address, it uses ARP to find it. Without ARP, local network communications wouldn’t function.
ARP Protocol Explained: The Basics
The ARP protocol is defined in RFC 826 and operates at Layer 2 (Data Link) of the OSI model. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
1. ARP Request
- A device sends out a broadcast to ask, “Who has this IP address?”
2. ARP Reply
- The device with that IP address responds with its MAC address.
3. Cache the Response
- The sender stores this info in the ARP table to avoid repeating the query.
💡 This entire process is automatic and happens in the background of every local area network (LAN) communication.
How ARP Works in Practice
Let’s say you’re accessing a file on a local server:
- Your computer knows the server’s IP address
- It sends an ARP request on the network
- The server responds with its MAC address
- Communication is established over Ethernet using that MAC
Here’s a simplified view of the ARP interaction:
less
CopyEdit
Device A (192.168.0.2) → Who has 192.168.0.10?
Device B (192.168.0.10) → I have it! My MAC is aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff
Why ARP Matters in Cybersecurity
ARP is simple—and that’s part of the problem. It doesn’t verify identities, making it a common target for attacks, particularly ARP poisoning attacks.
This vulnerability is especially concerning for:
- Healthcare organizations (HIPAA compliance)
- Financial services
- eCommerce businesses
- Enterprise networks
What Is an ARP Poisoning Attack?
Also known as ARP spoofing, this attack involves tricking a network device into associating the wrong MAC address with an IP address. This allows the attacker to intercept, modify, or stop data packets.
How It Works:
- An attacker sends forged ARP replies to the victim
- The victim updates their ARP cache with incorrect data
- All traffic meant for a legitimate device is sent to the attacker
Consequences:
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks
- Session hijacking
- Data theft or manipulation
- Network denial of service (DoS)
⚠️ ARP poisoning is a serious threat in environments without proper network segmentation or monitoring.
Signs of ARP Spoofing
Watch for:
- Duplicate IP address warnings
- Unusual traffic flow in your monitoring tools
- Sluggish network performance
- Inexplicable loss of packets
How to Protect Your Network from ARP Attacks
✅ Use Static ARP Entries
Assign fixed MAC addresses to specific IP addresses, especially for critical systems.
✅ Enable Packet Filtering
Use firewall rules to block ARP replies from unknown sources.
✅ Deploy Detection Tools
Install tools like:
- XArp
- Wireshark
- ARPWatch
✅ Network Segmentation
Use VLANs to separate sensitive devices and restrict ARP broadcast domains.
✅ Enable Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI)
A feature in enterprise-grade switches that validates ARP packets against DHCP snooping tables.
ARP in Modern IT Infrastructures
While modern networks like IPv6 have replaced ARP with Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), ARP is still foundational in IPv4 networks, which are still widely in use today.
ARP Table Management
Administrators should routinely:
- Inspect ARP caches
- Flush suspicious entries
- Use scripts to automate ARP monitoring
Actionable ARP Hardening Checklist
- 🔒 Set static ARP entries for key assets
- 🧰 Use ARP spoofing detection tools
- 🧱 Harden switches with Dynamic ARP Inspection
- 🌐 Segment networks with VLANs
- 🔁 Educate staff on social engineering that may facilitate spoofing
FAQs About ARP
1. What is ARP in simple terms?
ARP is a protocol that connects IP addresses to MAC addresses so devices on a local network can communicate.
2. What is an ARP poisoning attack?
It’s when a hacker sends fake ARP messages to link their MAC address with someone else’s IP, allowing them to intercept data.
3. How can I prevent ARP spoofing?
Use static ARP entries, detection tools, and enable Dynamic ARP Inspection on managed switches.
4. Is ARP used in all networks?
ARP is specific to IPv4 networks. IPv6 networks use a similar system called the Neighbor Discovery Protocol.
5. How do I check the ARP table?
On Windows, run arp -a in Command Prompt. On Linux/macOS, use arp or ip neigh.
ARP Awareness = Network Strength
Now that you understand what ARP is, you’re better equipped to secure your network’s foundation. Whether you’re in healthcare, finance, or tech, knowing how ARP works—and how attackers exploit it—is critical for modern cybersecurity.
🛡️ Ready to proactively protect your network against ARP-based threats?
👉 Sign up now with Itarian for advanced endpoint protection and network monitoring tools.