Why Every IT Leader Should Understand DNS
Updated on June 25, 2025, by ITarian
Have you ever wondered how you land on the right website just by typing its name into your browser? The answer lies in DNS, short for Domain Name System. It’s the backbone of your internet experience—and a critical component in your cybersecurity strategy.
In today’s hyper-connected world, understanding what DNS stands for isn’t just for techies. It’s essential knowledge for IT managers, cybersecurity teams, and business decision-makers aiming to secure digital assets.
What Does DNS Stand For?
DNS stands for Domain Name System—a hierarchical and decentralized naming system that translates human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into machine-readable IP addresses (like 192.0.2.1). Without DNS, we’d have to memorize long strings of numbers to navigate the web.
Think of DNS as the “phone book of the internet”—except it’s faster, smarter, and more vulnerable if not properly secured.
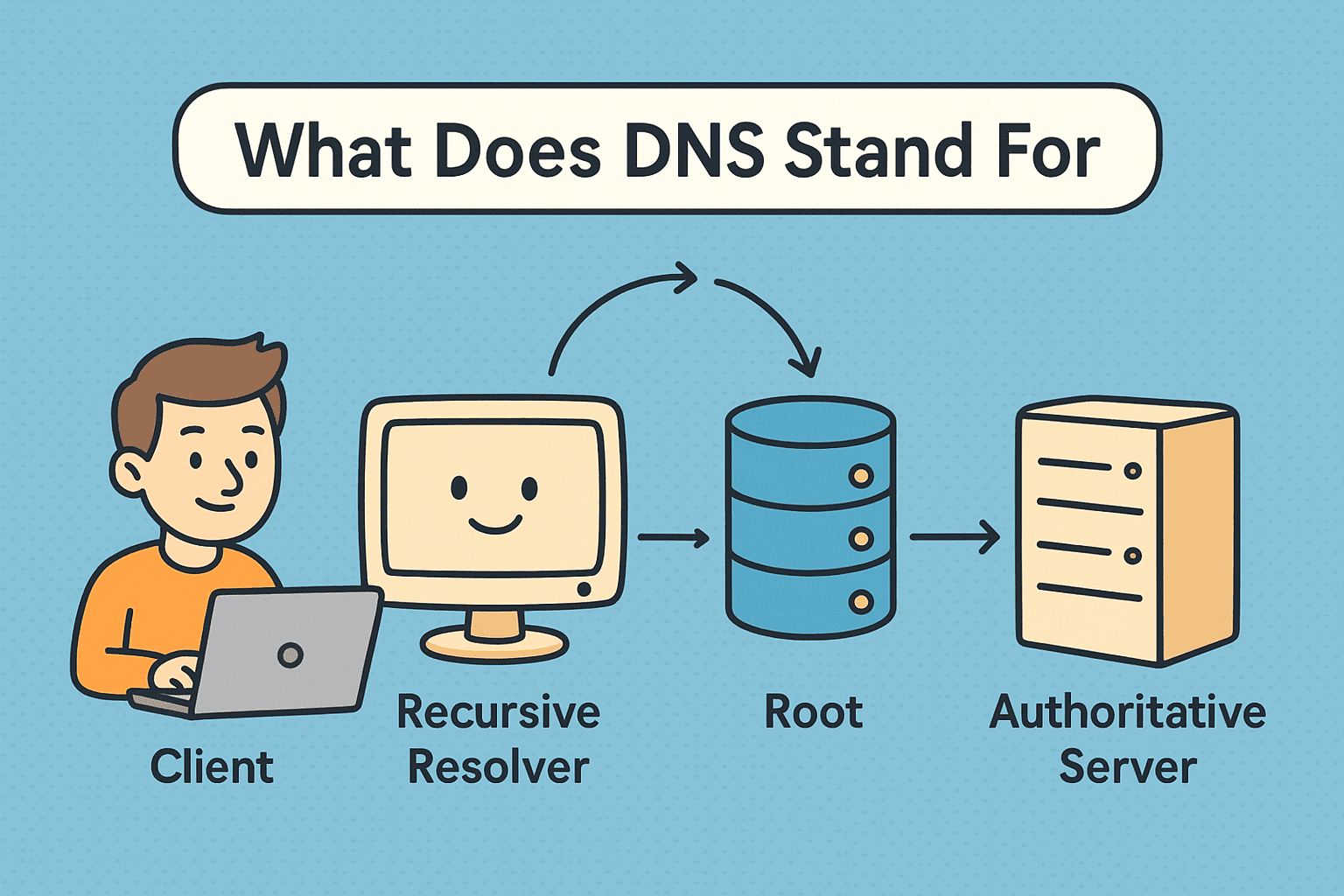
How the Domain Name System Works
Let’s break down the DNS process in a simple step-by-step format:
- DNS Query Initiation
A user types a website address into their browser. - DNS Resolver Check
The browser checks the local DNS cache to see if it already knows the IP address. - Recursive DNS Resolver
If the IP isn’t cached, a DNS request is sent to a recursive resolver (often maintained by ISPs or third parties like Google or Cloudflare). - Root Server Interaction
The resolver contacts a root name server, which directs it to a Top-Level Domain (TLD) server (e.g., .com, .org). - Authoritative DNS Server
The TLD server sends the query to the domain’s authoritative name server, which provides the correct IP address. - DNS Lookup Completion
The resolver returns the IP to the browser, which loads the website.
Why DNS Matters for Cybersecurity
DNS isn’t just a technical utility—it’s a frontline defense against cyber threats. Here’s why:
1. DNS as a Security Layer
Modern DNS services include DNS filtering, blocking access to malicious domains before a connection is made. This helps prevent phishing, ransomware, and other attacks.
2. DDoS Mitigation
DNS servers are common targets for Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. Proper DNS management helps absorb and deflect these attacks.
3. Zero Trust Architecture
In Zero Trust frameworks, DNS plays a critical role in verifying and logging access requests before connecting to internal or cloud-based resources.
Common DNS Record Types You Should Know
| Record Type | Purpose |
| A | Maps domain to IPv4 address |
| AAAA | Maps domain to IPv6 address |
| CNAME | Canonical name (alias of another domain) |
| MX | Mail exchange (used in email routing) |
| TXT | Arbitrary text, often used for SPF/DKIM |
Knowing how to configure these records can protect your domain from spoofing and improve email deliverability.
Real-World Use Cases: DNS in Action
✔️ Enterprise Network Monitoring
DNS logs are used by SOC teams (Security Operations Centers) to detect anomalies and potential breaches.
✔️ Remote Workforce Security
DNS filtering enforces safe browsing for remote teams, ensuring security even outside the company network.
✔️ Insider Threat Detection
Unusual DNS queries can help detect compromised insider accounts communicating with command-and-control servers.
DNS Lookup Tools: Stay One Step Ahead
Performing a DNS Lookup allows you to:
- Verify if your DNS records are correctly configured.
- Identify misconfigurations that could lead to downtime or vulnerabilities.
- Monitor DNS propagation across global servers.
Popular tools:
- MXToolbox
- Dig (Command Line)
- Google Admin Toolbox
Best Practices for DNS Security
- Use a reputable DNS provider (e.g., Cloudflare, Quad9, OpenDNS).
- Enable DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) to prevent spoofing.
- Regularly audit DNS records and remove obsolete entries.
- Segment DNS zones to reduce attack surfaces.
- Enable logging and real-time monitoring.
Actionable Tips for IT Managers and Cybersecurity Leads
- Integrate DNS into your SIEM tools for threat intelligence.
- Train your teams to recognize and respond to DNS anomalies.
- Automate DNS management to reduce errors and increase response time.
FAQs About DNS
1. What does DNS stand for in networking?
DNS stands for Domain Name System, which translates domain names into IP addresses in computer networks.
2. Why is DNS important in cybersecurity?
It acts as a first layer of defense by filtering malicious sites, enabling secure access control, and helping detect threats.
3. What is a DNS Lookup?
A DNS Lookup is the process of querying DNS servers to find the IP address linked to a domain name.
4. Can DNS be hacked?
Yes. Techniques like DNS spoofing or cache poisoning can mislead users to malicious sites, which is why DNS security is crucial.
5. What’s the difference between DNS and IP address?
DNS is a naming system for domains; IP addresses are numerical labels that computers use to identify each other.
Conclusion: DNS Is More Than Just Tech—It’s Strategy
Whether you’re a CISO, IT manager, or startup founder, understanding what DNS stands for and how it protects your infrastructure is non-negotiable. It’s your first line of defense—and potentially your biggest vulnerability.
🔐 Ready to enhance your DNS security?
Start protecting your business with industry-leading endpoint and DNS security solutions.
👉 Sign up now on Itarian