Boosting Laptop Speed by Upgrading RAM
Updated on October 29, 2025, by ITarian
Is your laptop running slower than usual when multitasking or handling large files? You’re not alone. Many users experience sluggish performance due to insufficient memory. Knowing how to upgrade RAM on laptop is one of the most effective ways to improve system speed, enhance productivity, and extend the device’s lifespan—without breaking the bank.
For cybersecurity experts, IT managers, and tech professionals, optimizing hardware isn’t just about performance—it’s about stability, reliability, and security. In this comprehensive post, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about upgrading your laptop’s RAM safely and efficiently.
Why Upgrading RAM Matters
RAM (Random Access Memory) is your laptop’s short-term storage—it temporarily holds data your system uses while running programs. The more RAM you have, the more data your system can process simultaneously, resulting in faster performance.
Key Benefits of a RAM Upgrade:
-
Faster performance: Reduces lag when multitasking or running heavy apps.
-
Improved system stability: Prevents crashes when using multiple programs.
-
Better compatibility with modern software: Keeps your system up to date with newer OS and security tools.
-
Enhanced cybersecurity performance: Allows endpoint protection tools to run efficiently without slowing down your device.
If your laptop struggles to run security applications, virtual machines, or large spreadsheets, it’s time to consider an upgrade.
How to Check Current RAM and Compatibility
Before learning how to upgrade RAM on laptop, you need to determine your system’s current memory configuration and its limits.
Step 1: Check Installed RAM on Windows
-
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
-
Go to the Performance tab.
-
Click Memory to view installed RAM and slot usage.
Alternatively:
-
Press Windows + R, type
dxdiag, and hit Enter. -
Under System Information, check the total memory available.
Step 2: Check RAM on macOS
-
Click the Apple menu → About This Mac.
-
Under Memory, view installed size, speed, and type.
Step 3: Identify RAM Type and Maximum Capacity
Every laptop has a limit on how much memory it can support.
Use tools like:
-
Crucial System Scanner (Windows & Mac)
-
CPU-Z (Windows)
-
System Information Utility (Mac/Linux)
These tools display:
-
Memory type (DDR3, DDR4, DDR5)
-
Clock speed (MHz)
-
Number of slots and occupancy
-
Maximum supported memory
Pro Tip: Visit your laptop manufacturer’s website for exact specifications—models differ even within the same product line.
Choosing the Right RAM for Your Laptop
Choosing the correct RAM ensures compatibility and stability.
1. RAM Type (DDR3, DDR4, DDR5)
Check your laptop’s motherboard support. You cannot mix RAM generations—for example, DDR4 RAM won’t fit into a DDR3 slot.
-
DDR3: Common in older laptops (pre-2016).
-
DDR4: Standard for most modern laptops.
-
DDR5: Found in high-end gaming and enterprise laptops.
2. RAM Speed (MHz)
Measured in megahertz (MHz), higher numbers mean faster data transfer. Match or exceed your current RAM speed for the best results.
3. RAM Capacity
Typical laptop configurations include:
-
8 GB – Suitable for basic productivity.
-
16 GB – Ideal for professionals and multitasking.
-
32 GB or more – Recommended for cybersecurity labs, virtualization, or heavy software workloads.
4. Form Factor (SO-DIMM)
Laptops use SO-DIMM (Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module) sticks, which are smaller than desktop DIMMs. Ensure you buy the right physical size.
Preparing to Upgrade RAM
Before installing new RAM, take precautions to protect both your device and the new module.
Tools You’ll Need:
-
Small Phillips-head screwdriver
-
Anti-static wrist strap (to prevent electrostatic discharge)
-
Clean, flat workspace
Precautions:
-
Back up your data. Although RAM upgrades are low-risk, it’s always smart to secure your files.
-
Disconnect all power sources. Unplug the charger and remove the battery (if removable).
-
Ground yourself. Static electricity can damage internal components.
Step-by-Step Process: How to Upgrade RAM on Laptop
Now, let’s go through the actual installation process.
Step 1: Power Down and Unplug
Shut down your laptop completely. Remove all cables, external devices, and the battery (if possible).
Step 2: Open the Laptop Case
Flip your laptop upside down and locate the access panel or bottom cover.
-
Some laptops have a dedicated RAM compartment.
-
For newer ultrabooks, you may need to remove the entire bottom cover using a precision screwdriver.
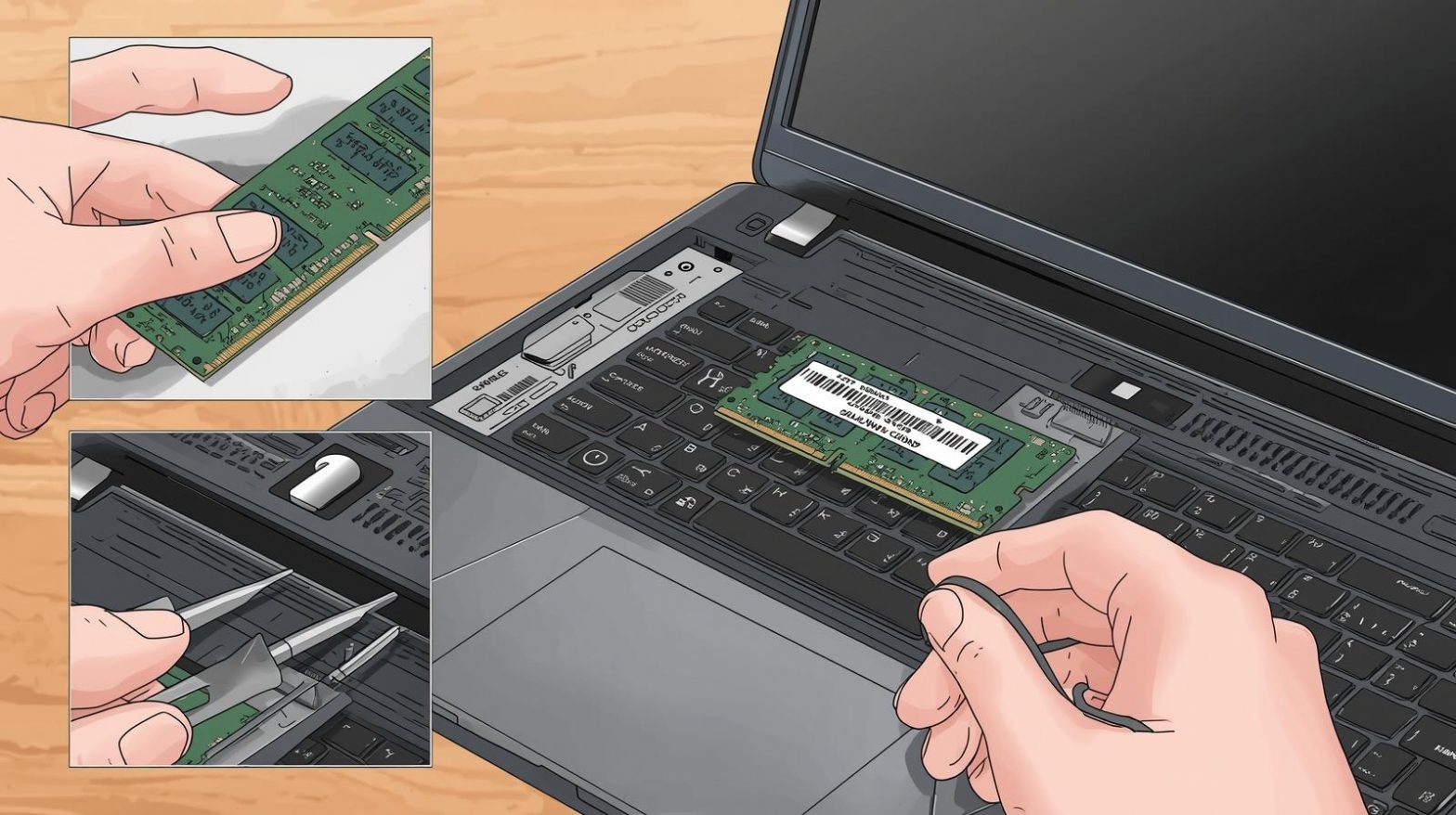
Step 3: Locate the RAM Slots
Once the cover is off, look for small rectangular modules inserted into angled slots—these are your RAM sticks.
Step 4: Remove the Old RAM (If Necessary)
-
Gently push the side clips outward to release the module.
-
The RAM will pop up at an angle.
-
Pull it out carefully by the edges—avoid touching the gold contacts.
Step 5: Insert the New RAM
-
Align the notch on the RAM with the slot.
-
Slide the module in at about a 30-degree angle.
-
Press down until the clips lock it securely in place.
Ensure both modules are seated evenly and firmly.
Step 6: Reassemble and Reboot
Replace the cover and battery, then reconnect power. Power on the laptop.
If everything is installed correctly, your system should boot normally.
Verifying the Upgrade
After booting, verify the system recognizes the new memory.
On Windows:
-
Open Task Manager → Performance → Memory.
-
Confirm the new total memory amount.
On Mac:
-
Click Apple Menu → About This Mac.
-
Under Memory, check the updated RAM capacity.
If the system doesn’t recognize the new RAM:
-
Ensure the module is fully seated.
-
Verify compatibility (type, speed, capacity).
-
Try each stick individually to test for faults.
Performance Gains After Upgrading RAM
Once you’ve learned how to upgrade RAM on laptop, you’ll notice performance improvements in several areas:
1. Faster Multitasking
Run multiple applications like browsers, antivirus, and productivity tools simultaneously without lag.
2. Improved Virtualization
Virtual machines and security sandboxes require high memory bandwidth—extra RAM ensures smoother performance.
3. Better Gaming and Media Editing
RAM-intensive software like Adobe Premiere Pro or CAD tools run faster and crash less often.
4. Enhanced System Security
Security software like endpoint protection or network monitoring tools consume memory. With more RAM, your system remains responsive while maintaining full protection.
Upgrading RAM on Specific Laptop Brands
Each manufacturer designs laptops differently. Below are brand-specific notes.
Dell / HP / Lenovo
-
Most models feature easy-access RAM panels.
-
Use matching RAM pairs for dual-channel performance.
-
Dell Precision and HP ZBook series support up to 64 GB.
Apple MacBook
-
Newer MacBooks have soldered RAM, meaning upgrades are impossible post-purchase.
-
Older models (pre-2016) allow upgrades—consult Apple’s support page for specs.
ASUS / Acer / MSI
-
Some ultrabooks combine soldered and removable RAM. Check if your model includes at least one upgradeable slot.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Buying incompatible RAM – Always verify your laptop’s supported type and maximum capacity.
-
Mixing different speeds or brands – Stick to identical RAM models for stability.
-
Forgetting static protection – Use an anti-static strap or touch grounded metal before handling components.
-
Ignoring BIOS updates – Some laptops require BIOS updates to support new memory configurations.
-
Not seating RAM properly – A loose module may cause boot failures or blue screen errors.
RAM Upgrade Alternatives
If your laptop’s RAM is non-upgradable (e.g., soldered), consider these alternatives:
-
Optimize Startup Programs: Disable unnecessary applications using Task Manager.
-
Increase Virtual Memory: Set up a pagefile in Windows to simulate RAM using disk space.
-
Upgrade to an SSD: Faster read/write speeds can offset limited memory.
-
Use Cloud-Based Environments: Offload heavy computing tasks to cloud servers.
Security and IT Management Perspective
From a cybersecurity or IT standpoint, upgrading RAM helps maintain endpoint performance under security loads.
-
Faster malware scanning: More RAM allows antivirus programs to analyze data efficiently.
-
Improved patching and compliance: Systems with sufficient memory handle software updates smoothly.
-
Enhanced monitoring: Endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems perform real-time analysis without lag.
In enterprise networks, combining hardware optimization with endpoint security platforms like ITarian ensures reliability and defense against evolving threats.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I mix different RAM sizes or speeds?
Yes, but it’s not ideal. The system will default to the lowest speed, and mismatched RAM can cause instability.
2. How much RAM does my laptop need?
-
8 GB is sufficient for general use.
-
16 GB is recommended for business and IT operations.
-
32 GB or more suits heavy virtualization or cybersecurity workloads.
3. Will upgrading RAM void my warranty?
In most cases, no—unless you damage the system during installation. Check your manufacturer’s policy.
4. Can I upgrade RAM on ultrabooks or MacBooks?
Some ultrabooks and modern MacBooks have soldered RAM, making upgrades impossible. Always verify before purchasing.
5. How do I know if my RAM is bad?
Use Windows Memory Diagnostic or MemTest86 to detect errors or faulty modules.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how to upgrade RAM on laptop is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to enhance speed, multitasking, and overall performance. Whether you’re an IT manager running security tools or a business leader optimizing workflow, increased memory capacity ensures smoother, more reliable operations.
Upgrading your RAM doesn’t just improve productivity—it also strengthens endpoint performance and supports advanced cybersecurity software without performance trade-offs.
Ready to take control of your system’s performance and protection?
Start your free ITarian trial today.