Endpoint Security
We have partnered with our sister company Xcitium, who offers the most complete protection against ransomware leveraging patent pending auto-containment technology. This is how to neutralize endpoint attacks without any productivity or business disruption. Secure your network with EDR.
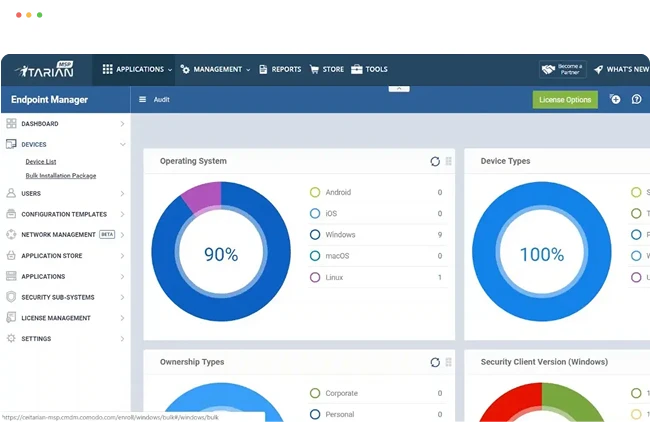
Endpoint Security with Patented Zero Trust Technology
Traditional endpoint security solutions are detection-based, and thus cannot prevent new malware from entering your environment. However, we’ve developed an approach to safeguarding you from new malware, by automatically containing all unknown executables to virtualized instances, where they can do no damage.
Utilize advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence to detect and respond to threats in real-time. Our platform identifies and neutralizes threats before they can cause harm.
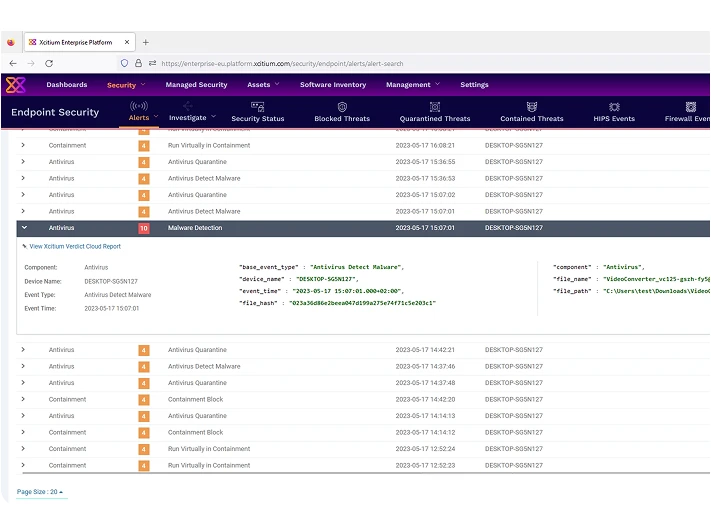
Defend against known and unknown malware with our multi-layered approach. Xcitium Endpoint Security leverages behavioral analysis and heuristic scanning to prevent infections.
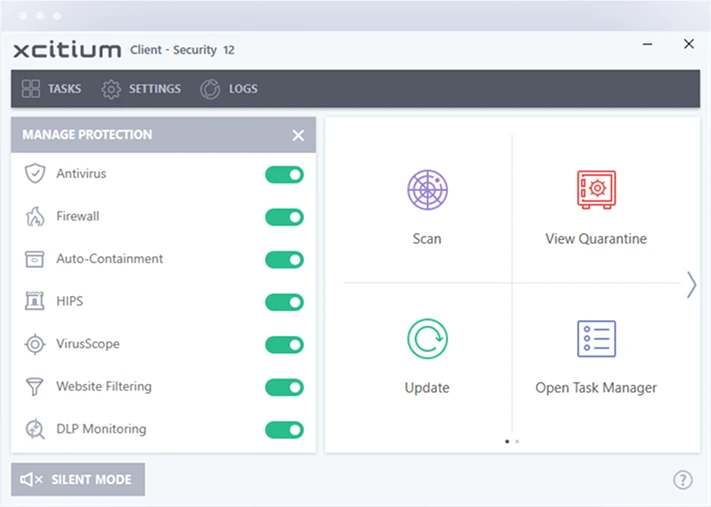
Minimize the impact of security incidents with automated response capabilities. Xcitium Endpoint Security quickly contains and mitigates threats, reducing downtime and operational disruption.
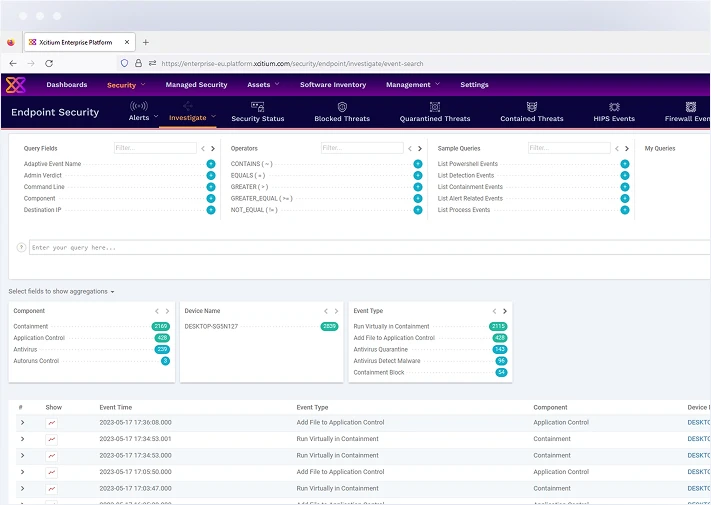
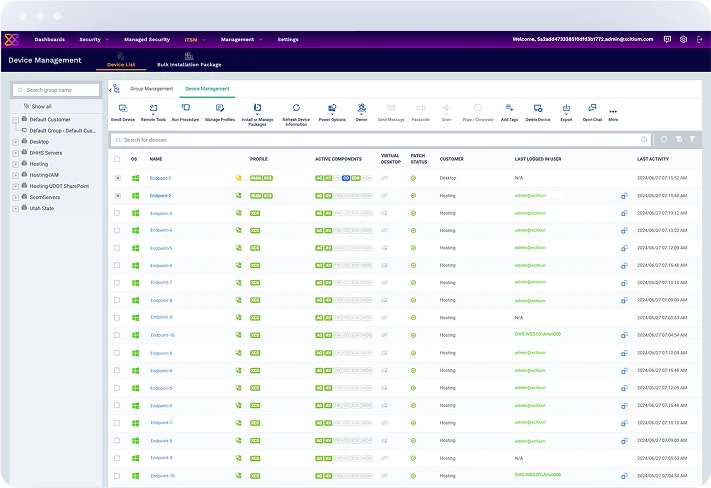
Manage and secure all endpoints from a single, unified console. Simplify IT operations with centralized control over device policies, updates, and security configurations.
Why Choose ITarian?
Choose ITarian for its seamless scalability, allowing educational institutions to manage and secure endpoints across multiple campuses with ease. Its automated tools reduce the burden on IT teams, ensuring a smooth, secure, and efficient learning environment for both students and staff.
